Learner
THE FUNDAMENTAL OF COMPUTER

THE FUNDAMENTAL OF COMPUTER
MONITOR C.P.U
( Visual Display Unit) (Central Processing Unit)

KEYBOARD U.P.S
(Input Device) (Uninterrupted Power Supply)
MOUSE SPEAKER
(Input Device) (Input Device)
Evolution and History of Computers:
- The earliest known device for calculation is Abacus. It is with 10 beads stung into the wires attached to frame and it used to perform simple calculations.
- In 1642, Blaise Pascal developed the first basic calculator which would do limited jobs.
- In 1690, Leibnitz developed a machine that could perform addition, subtraction ,multiplication, division and square root functions.
- In 1822, Charles Babbage built a model called difference engine, it performs calculations without human intervention. After that, in 1833, Babbage designed a machine called Analytic Engine. It had an arithmetic unit to perform calculations and mechanism to store results and instructions and it provide the base for evolution of modern computers. Because of such contributions Babbage is known is the father of the modern computers.
- During late 1940’s, on Von Neumann found the concept of stored program and encoding of instructions in the language.
- In 1946, J Presper Eckert and John W Mauchly invented ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator) machine at university of Pennsylvania. ENIAC was the first machine to use large no. of vacuum tubes. The machinery required a big space and lot of energy to keep it cool.
Generations of Computers:
Each generation of computer is characterized by a major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate, resulting in increasingly smaller, cheaper, and more powerful and more efficient and reliable devices.
First Generation (1945-1955):

Vacuum Tubes The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory, and were often enormous, taking up entire rooms. They were very expensive to operate and in addition they uses a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions. The first generation of computers started with ENIAC, it was then followed by the IBM UNIVAC-I (Universal Automatic Computer) built by J. Presper Eckert and John W Mauchly in 1951, used for business data processing.
Second Generation (1955-65):

To overcome difficulties in the first generation computers, transistors replaced vacuum tubes. The transistor was far superior to the vacuum tube, allowing computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient and more reliable than their first-generation computers. Example: IBM 1620
Third Generation (1965-80):

Integrated Circuits(IC’s) The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers. Transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips, called semiconductors, which drastically increased the speed and efficiency of computers. Example: IBM 360, PDP 8 and PDP 11 Machines.
Fourth Generation (1980-89):

Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) This generation of computers used large scale IC’s called Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI), as it became possible to build thousands of integrated circuits built onto a single silicon chip. Because of these, they were faster, smaller, reliable and became more user friendly, and widely used in personal applications, hence such machines were called personal computers. Example: Apple-II, CRAY Series Super Computers and IBM PC etc.
Fifth Generation (1989-Till date):

Artificial Intelligence (AI) These computers made smarter in terms of processing speed, user friendly and connectivity to the network. These computers are portable and very sophisticated. These computers used advanced software technologies, such as parallel and distributed operating systems and artificial intelligence. Example: Intel PC’s, PARAM 10000 and IBM Notebook etc.
Definition of Computer: Computer (Commonly Operated Machine Particularly Used for Technology Education and Research) is a digital electronic device which takes inputs from the user (i.e., instructions), processes the data and gives the exact output to the user (i.e., results). Basically, computer can perform the following operations:
Taking the input in the form of instruction and data.
· Process the instruction and data and stores the results.
· Displays or prints the stored results in the desired format
. Characteristics:
Speed: Computer speed depends upon the type of processor and bus line architecture used. Good type of processor and bus line architecture can executes millions of instructions in one second. Processor speed can be measured in terms of GHz (Giga Hertz).
Accuracy: Computer can perform millions of operations with the given input set of instructions and data, and the results can be produced accurately without giving any errors.
Reliability: Computer communication and components are very reliable and has very less failure rate.
Storage: Two types of storage are used, first is primary storage and second is secondary storage. Primary storage stores the data temporarily for executing the processes i.e. RAM, and secondary storage is used for permanent storage of data i.e. hard disk. Some external devices are also used to store data like portable hard disk, pen drives, memory card etc.
Automation: Once a set of programs is fed into the computer, then the computer can take decision automatically without interfering with the user. Example: Pen drive drivers are automatically detected and loaded called as auto play.
Versatility: Computers are capable of performing various operations at same time. Like you are reading this webpage and downloading two files from the internet and also printing the documents simultaneously.
Diligence: Computer can work lot of hours with the same speed and produces accurate results for each operation, without getting tired.
Limitations:
- Computer are not intelligent, they need to be programmed to do their task.
- They cannot learn from their experience
Applications of Computers :
The computer is used to assist man in business organizations, research centers and in many parts of human life. Computers are applied in many organizations are as follows.
Scientific Research: Computers are now standard feature of life in universities and industrial laboratories and scientific establishment. Example: Forecasting, temperature and air pressure, medical research and industrial laboratories.
Business applications: Computer aided design (CAD), word processors and databases are the examples for these applications. Word processors are very useful in data entry work. Databases are useful in accounts i.e. just like a payroll accounts etc.
Office automation: Office automation covers the use of standalone word processors, personal computers, work stations, terminals, various peripheral devices, networks and fax systems. These are used for document preparation, desktop publishing, electronic mail, document storage and retrieval, data and voice communication, business packages and information management etc.
Stock Controls and sales: Stock control, the processing of sales orders and sales accounting, sales accounting, market research forecasting and subsequent production planning are the areas.
Banking: Computers are used in banking for storing the customer’s records, bank records and calculate the interest rates and produces the manager’s report and produces the statements etc. Bank transactions can also be processed.
Insurance: Computers are very useful in insurance companies for recording data and for producing reports.
Educational and research: The use of computers at various levels of academic and education have applied to import knowledge to students in highly scientific and practical manner.
Transport and communication: The flow of vehicular traffic, cargo, people in transit from one place to another are being effectively monitored through computers to prevent crowding, traffic jams, over loading and avoiding delays.
Computer Organization: A computer can process data, pictures, sound (voice) and graphics. They can solve highly complicated problems quickly and accurately. A computer has the components and as shown in below Fig. Performs basically five major computer operations or functions:
- It accepts data or instructions from user.
- It controls all operations inside a computer.
- It can process data as required by the user.
- It stores data and
- It gives results in the form of output.
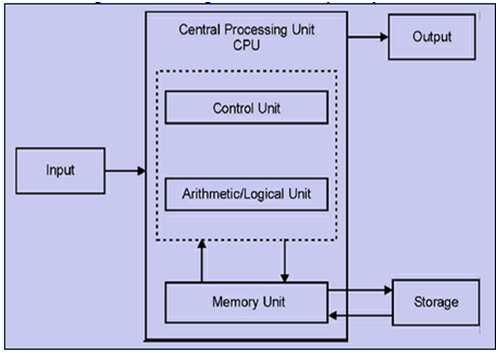
Input Unit: Input Unit devices, accepts the instructions and data from the user. Then it converts these instructions and data into its equivalent computer acceptable form, after that it supplies the converted instructions and data to the computer system for further processing. Example: Keyboard, Mouse, Touch screen, Joystick and Track ball etc.
Central Processing Unit: The control unit and ALU of a computer system are jointly known as the CPU. The CPU is the brain of computer system. It takes all calculations and comparisons in a computer systems and it is also responsible for activating and controlling the operations of other units of computer system.
Arithmetic Logical Unit: An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a digital circuit that performs arithmetic and logical operations. The ALU is a fundamental building block of the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer, and ALU can perform the integer arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division), logical and comparisons operations.
Control Unit: The control unit (often called a control system or central controller) directs the various components of a computer. It reads and interprets (decodes) instructions in the program one by one. The control system decodes each instruction and turns it into a series of control signals that operate the other parts of the computer.
Memory Unit: The Memory Unit is the part of the computer that holds data and instructions for processing. There are two types of computer memory inside the computer:
Primary Memory and Secondary Memory.
Primary storage, presently known as main memory, is the only one directly accessible to the CPU. Secondary storage, sometimes called auxiliary storage, is all data storage that is not directly accessible to the processor but uses the I/O channels.
Output Unit: The output unit is just reverse of the input unit. It accepts the result produced by computer, which are in coded form and can't be easily understood by us. So that, it converts these coded results into human readable form. After that it supplies the converted results to the outside world. Example: Monitor, Printer, Plotter, and Speakers etc.
Computers Classification:
Types of computers classified on based upon the purpose, data processing, and size of the computer. Accordingly they are classified into as follows:
1. Analog Computers: Analog computers are those that represent data in a Continuous manner using physical variables such as pressure, temperature etc. These classes of computers are used for scientific/engineering purposes and are not concerned with commercial data processing.
A good example of this class of computer is the computer used in hospitals for measuring blood pressure of patients, also a filling station gasoline pumps work purely on analog processes.
2. Digital Computers: These are computers that represent data in discrete or discontinuous manner using binary system. A digital watch is an example of a digital device. The output from Digital computers are usually in the form of discrete values. This class of computers is commonly found in the business environments, and they include Desk calculators, Adding machines, and most of the computers we have around (IBM, BBC, Radio Shack Personal Computers (PC), Laptops, and Desktops etc.
3. Hybrid Computers: As the name implies, this class of computers combines the features of both digital and analog computers. Their outputs could be in the form of discrete or continuous value or a combination of both. This class of computers is commonly found in highly scientific environments.
4. Modern Computers: Modern computers are classified as follows.
1. Super computers
2. Mainframe computers
3. Mini computers
4. Micro computer
Super computers:
Most powerful computers characterized as fastest, very high processing speed and of large data storage.
Specifically used for complex applications by big organization.
Good example is NASA and ISRO uses supercomputers to track and control space discovery.
Mainframe computers :
Capable of performing high processing speed and data storage but not powerful as super computers.
Wired in air-conditioned rooms.
Example: ISP providers use mainframe computers to process information about millions of internet users.
Mini computers :
Less processing speed than mainframe computers.
Departments of large company’s use this type of computers.
They can handle large database and accounting efficiently.
Example: Department of computer monitoring the network traffic of whole company.
Micro computers :
Least powerful type of computers but are the most widely used and growing in the fastest rate. Hardware peripherals can be attached easily.
Includes Desktop computers (PC’s), Laptops, tablet PC's, Personal Digital Assistants (PDA) etc.
Computer Peripherals/Hardware: The hardware is the physical and visible components of the computer system. Peripheral components classified as:
Input Devices: An input device is hardware device that sends data to a computer, allowing you to interact with and control the computer. The following are the some of input devices listed below:
1. Keyboard: The keyboard is a way to input letters or numbers into different applications or programs. A keyboard also has special keys that help operate the computer.
2. Mouse: The mouse is used to open and close files, navigate web sites, and click on a lot of commands (to tell the computer what to do) when using different applications.
3. Joystick: A joystick is used to move the cursor from place to place, and to click on various items in programs. A joystick is used mostly for computer games.
4. Digital Camera: A digital camera can be used to take pictures. It can be hooked up to a computer to transfer the pictures from the camera to the computer.
5. Microphone: A microphone is used to record sound. The sound is then saved as a sound file on the computer.
6. Scanner: A scanner is used to copy pictures or other things and save them as files on the computer.
7. Barcode reader: A bar code scanner scans a little label that has a bar code on it. The information is then saved on the computer. Bar code scanners are used in libraries a lot. 8. Light Pen: Light pen is a pointing device which is similar to a pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or draw pictures on the monitor screen.
Output Devices: An output device is any peripheral that receives data from a computer, usually for display, projection, or physical reproduction. An output given by the computer can be in the form of a display on the screen or a printed document or a song that is played. The following are the some of the output devices listed below:
1. Monitor: A monitor is also called as video display terminal (VDT). It visually displays the processed data, and that can be viewed by users on the monitor. There are two types of computer monitors available, namely CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) and flat panel (LCD-Liquid Crystal Display) monitors. All monitors rely in a video card, which is located on the motherboard to display the information. It is the video card, which processes the data into images, which is eventually displayed on the monitor.
2. Printers: The next of the computer output devices is the printer, which is an external hardware device, which takes processed data from the computer to generate a hard copy of the data. After the monitors, printers are the most used peripherals on computers and they are commonly used to print text data, images, etc. There are three main types of computer printers, namely ink jet, laser printers and dot matrix. Each of these printer types uses a different technology to print the data.
3. Plotters: A plotter is a computer hardware device much like a printer that is used for printing vector graphics (i.e. drawing images). Instead of the traditional toner, plotters use a pen, pencil, marker, or other writing tool to draw a design onto paper. In general, plotters are considerably more expensive than printers. They are used in engineering applications where precision is mandatory.
4. Speakers: A speaker is a hardware device that is connected to a computer’s sound card, which outputs sound generated by the card. Audio data generated by the computer is sent to the audio card that is located in the expansion slot. The card translates the data into audio signals, which are then sent to either the speakers or headphones.
5. Projector: It is a hardware device, with which an image like a computer screen is projected onto a flat screen. Image data is sent to the video card, by the computer which is then translated into a video image and sent to the projector. A projector is often used in meetings or to make presentations, because they allow for a large image to be shown, with which the display is available for a large audience.
WINDOWS
Microsoft window popularly known as MS window or simply window is one of the most popular operating system.
The operating system controls and allows computer to do all necessary works.
Work of window:-
- It control the hardware [ keyboard, monitor, mouse]
- It controls the operation of the software such as MS Word, MS Paint.
- It receives input from output device [keyboard, mouse etc.] and send it to the output [monitor, printer etc.]
Desktop
The window desktop is the screen with a lot of icons on it a window is the rectangular area in which a content of document is displayed.

Computer Field
- Software
- Hardware
- Networking
Software
We cannot see as well as touch. For example:- power point, c, c++, tally , etc.
Hardware
All machinery parts of computer that we can see and touch. For example :- monitor, keyboard, C.P.U [Central processing unit], mouse, etc.
Networking
To connect two or more than two computer through networking for example:-
LAN = Local area network
MAN= Metro Politian area network
WAN= Wide area networking
MS PAINT
PAINT:- A graphic program that enables you to draw pictures on the display screen. Most paint program provides the tools shown below in the form of icons. By selecting an icon, you can perform functions. Circle and ovals. These applications support many of the features of draw programs, such as the ability to work with objects. Microsoft Paint is a graphics- editing program included with Windows operating systems. Paint allows you to create graphics on your computer using several different tools, including brushes, text and erasers.
HOME

Color:-It is used to fill color. The “color 1” slot represents the foreground color. The “color2” slot represents the background color.
Paint bucket:- It is used to fill color. In selected area.
Brush: -Click and drag the mouse in the drawing area to draw using the slected tool.

Shapes:- It also provides easy ways to draw common shapes such as straight lines, rectangles, circles and ovals.

Eraser:- Click and drag the eraser to remove everything.